If pilots, soldiers, and astronauts rely on simulated environments to train for critical decisions, why can’t doctors learn the same way?
A simulation-driven education platform that bridges clinical exposure gaps and transforms teaching and learning through case-based, AI-generated content.
Tools
Svelte, fastAPI, Supabase, OpenAI/Gemeni APIs, Figma, Figjam, Cursor
Tools
Svelte, fastAPI, Supabase, OpenAI/Gemeni APIs, Figma, Figjam, Cursor
Tools
Svelte, fastAPI, Supabase, OpenAI/Gemeni APIs, Figma, Figjam, Cursor
Responsible for
Product Strategy, Design and Developement
Responsible for
Product Strategy, Design and Developement
Responsible for
Product Strategy, Design and Developement
Team
CCO - Dr Gopikrishnan Anjaneyan CTPO - Cyril Varghese CBO - Naresh Shetty
Team
CCO - Dr Gopikrishnan Anjaneyan CTPO - Cyril Varghese CBO - Naresh Shetty
Team
CCO - Dr Gopikrishnan Anjaneyan CTPO - Cyril Varghese CBO - Naresh Shetty



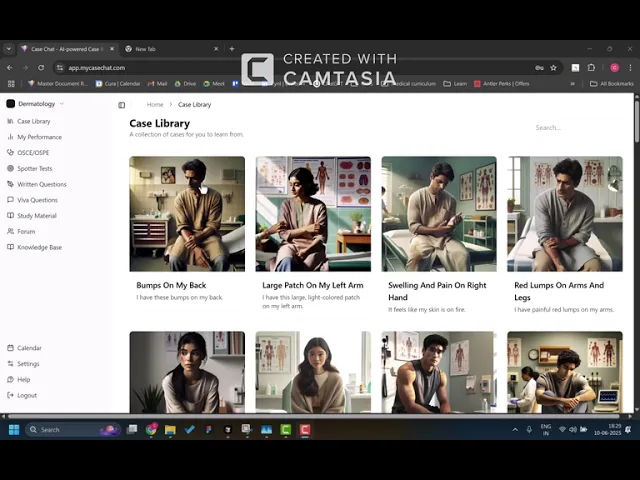
A library of cases and patients to learn from
A library of cases and patients to learn from
Project Context
Project Context
Project Context
Medical students often lack safe, hands-on ways to practice clinical decision-making.
CaseChat is an experiential learning platform that simulates digital patients in clinical environments, allowing medical students to learn by treating cases, making mistakes, and refining their reasoning like real doctors but without real-world consequences.
Medical students often lack safe, hands-on ways to practice clinical decision-making.
CaseChat is an experiential learning platform that simulates digital patients in clinical environments, allowing medical students to learn by treating cases, making mistakes, and refining their reasoning like real doctors but without real-world consequences.
Medical students often lack safe, hands-on ways to practice clinical decision-making.
CaseChat is an experiential learning platform that simulates digital patients in clinical environments, allowing medical students to learn by treating cases, making mistakes, and refining their reasoning like real doctors but without real-world consequences.



A virtual clinic has all the ingredients of an ideal learning environment
A virtual clinic has all the ingredients of an ideal learning environment
Demo
Demo
Demo

Problem Discovery
Problem Discovery
Problem Discovery
We started with a RAG-based tool for classroom prep that my cofounder, a teaching doctor, thought would be useful.
But when we tested it, we found that the bigger challenge wasn’t quality classroom content, it was the lack of clinical learning resources.
Students had little exposure to real patient cases and no environment to learn from mistakes.
We started with a RAG-based tool for classroom prep that my cofounder, a teaching doctor, thought would be useful.
But when we tested it, we found that the bigger challenge wasn’t quality classroom content, it was the lack of clinical learning resources.
Students had little exposure to real patient cases and no environment to learn from mistakes.
We started with a RAG-based tool for classroom prep that my cofounder, a teaching doctor, thought would be useful.
But when we tested it, we found that the bigger challenge wasn’t quality classroom content, it was the lack of clinical learning resources.
Students had little exposure to real patient cases and no environment to learn from mistakes.
Solution
Solution
Solution
To address this gap, we built an AI powered case simulation engine that mimics a virtual clinical environment.
Instead of just generating classroom content,
the platform turned clinical cases into interactive patient encounters.
Students could practice clinical reasoning hands on, making decisions, learning from mistakes, and absorbing theory in context and learning concepts integrated manner.
To address this gap, we built an AI powered case simulation engine that mimics a virtual clinical environment.
Instead of just generating classroom content,
the platform turned clinical cases into interactive patient encounters.
Students could practice clinical reasoning hands on, making decisions, learning from mistakes, and absorbing theory in context and learning concepts integrated manner.
To address this gap, we built an AI powered case simulation engine that mimics a virtual clinical environment.
Instead of just generating classroom content,
the platform turned clinical cases into interactive patient encounters.
Students could practice clinical reasoning hands on, making decisions, learning from mistakes, and absorbing theory in context and learning concepts integrated manner.



Cases are created by doctors and students experience them as interactive experiences
Cases are created by doctors and students experience them as interactive experiences
Cases are created by doctors and students experience them as interactive experiences
Iteration & Final Solution
Iteration & Final Solution
Iteration & Final Solution
The product evolved step by step:
Diagnose & Feedback – The first version let students interact with a virtual patient and practice making a diagnosis and get feedback.
Treat and Learn Theoretical Concepts – We then added treatment decisions and layered in theoretical concepts so students could learn while solving the case.
Assessment added – Finally, we introduced MCQ-based OSCE assessments to mirror exam patterns and test what students had learned.
Together, these iterations turned the product into a holistic learning experience, helping students build deep clinical reasoning skills while also preparing for exams.
The product evolved step by step:
Diagnose & Feedback – The first version let students interact with a virtual patient and practice making a diagnosis and get feedback.
Treat and Learn Theoretical Concepts – We then added treatment decisions and layered in theoretical concepts so students could learn while solving the case.
Assessment added – Finally, we introduced MCQ-based OSCE assessments to mirror exam patterns and test what students had learned.
Together, these iterations turned the product into a holistic learning experience, helping students build deep clinical reasoning skills while also preparing for exams.
The product evolved step by step:
Diagnose & Feedback – The first version let students interact with a virtual patient and practice making a diagnosis and get feedback.
Treat and Learn Theoretical Concepts – We then added treatment decisions and layered in theoretical concepts so students could learn while solving the case.
Assessment added – Finally, we introduced MCQ-based OSCE assessments to mirror exam patterns and test what students had learned.
Together, these iterations turned the product into a holistic learning experience, helping students build deep clinical reasoning skills while also preparing for exams.






